How a 4 Stroke Engine Works...
Suck, Squeeze, Bang, Blow!! (Sounds like an advert for a porn movie, but this is a simplified version of the 4 stroke theory!)
A Very Basic 4 Stroke Engine
Please note-the diagram below represents a very simple version of a 4 stroke motorcycle engine, in reality, they are a little bit more complicated!!!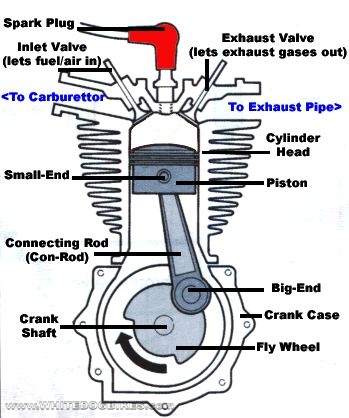
Engine Terminology
A Longer list of commonly used Engine Terminology is available HERE(link will open in a new window)
Stroke: Either the up or down movement of the piston from the top to the bottom or bottom to top of the cylinder (So the piston going from the bottom of the cylinder to the top would be 1 stroke, from the top back to the bottom would be another stroke)
Induction: As the piston travels down the cylinder head, it 'sucks' the fuel/air mixture into the cylinder. This is known as 'Induction'.
Compression: As the piston travels up to the top of the cylinder head, it 'compresses' the fuel/air mixture from the carburettor in the top of the cylinder head, making the fuel/air mix ready for ignighting by the spark plug. This is known as 'Compression'.
Iginition: When the spark plug ignites the compressed fuel/air mixture, sometimes reffered to as the power stroke.
Exhaust: As the piston returns back to the top of the cylinder head after the fuel/air mix has been ignited, the piston pushes the burnt 'exhaust' gases out of the cylinder & through the exhaust system.
The 4 Stroke Cycle
We have simplified this explanation as much as possible so some of the 'correct' terms have been replaced. There are many more factors which enable an engine to run, such as fuel/air ratios, ignition timing & shaped piston heads (extensively used in 2 stroke engines) but the explanation below outlines the basic differences between 2 & 4 stroke engine operation.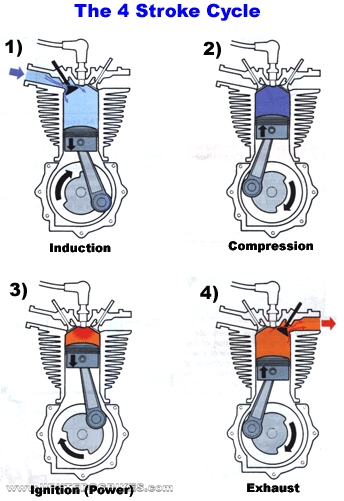
Stroke
|
Piston Direction
|
Inlet & Exhaust Valve Positions
|
Actions Occurring During This Stroke
|
Explanation
|
Stroke 1
|
Piston travels down the cylinder barrel
|
Inlet valve open/Exhaust valve colsed
|
Induction stroke
|
As the Piston travels down the cylinder barrel, the inlet valve opens & fresh fuel/air mixture is sucked into the cylinder
|
Stroke 2
|
Piston travels up the cylinder barrel
|
Inlet & exhaust valve closed
|
Compression stroke
|
As the piston travels back up the cylinder, the fresh fuel/air mix is compressed ready for ignition
|
Stroke 3
|
Piston travels down the cylinder barrel
|
Inlet & exhaust valve closed
|
Ignition (power) stroke
|
The spark plug ignites the compressed fuel/air mix, the resulting explosion pushes the piston back to the bottom of the cylinder
|
Stroke 4
|
Piston travels up the cylinder barrel
|
Inlet valve closed/Exhaust valve open
|
Exhaust stroke
|
As the piston travels back up the cylinder barrel, the spent exhaust gases are forced out of the exhaust valve
|
No comments:
Post a Comment